 Initial construction
Initial construction
- Singapore Improvement Trust (SIT) and Housing and Development Board (HDB) built 20 New Towns (10,000-70,000 units) and about 80-100 small estates (under 10,000 units).
- Economic Development Board (EDB) built between 1964 and 1968; together with Jurong Town Corporation (JTC) between 1968 and late 1970s 5 estates in Jurong and Sembawang industrial areas.
- Housing and Urban Development Company (HUDC) built between 1974 and 1987 22 estates totaling about 9,800 units, sandwich housing for middle-income people who did not qualify for HDB flats but could not afford a private property. List of HUDC estates.
HDB took over JTC and HUDC in 1982, becoming sole provider of public housing in Singapore. The last 12 HUDC estates were actually built by HDB.
The HDB Annual Reports up to 1989 display a list of about 100 estates.
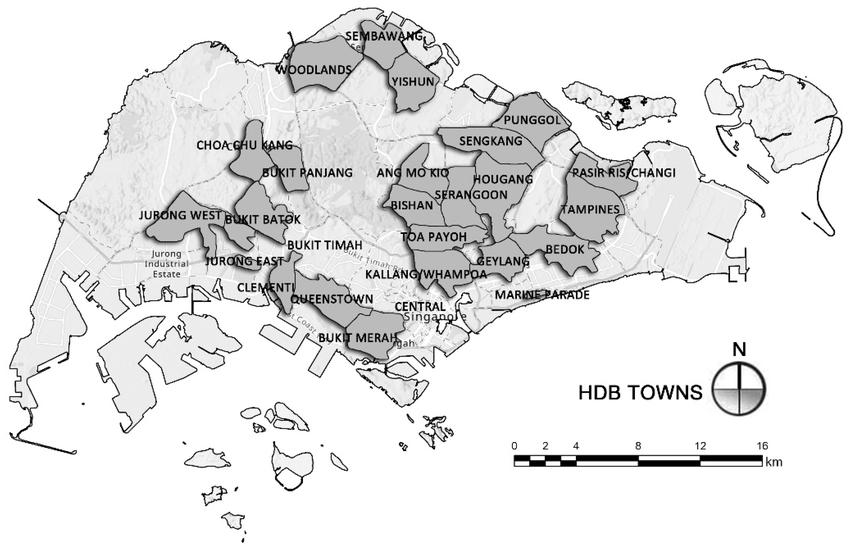
URA defined 55 Planning Areas in 1991 and the ~100 estates were re-organized:
- AR 1990 showed 20 New Towns: Ang Mo Kio, Bedok, Bishan, Bukit Batok, Bukit Merah, Bukit Panjang, Choa Chu Kang, Clementi, Geylang, Hougang, Jurong East, Jurong West, Kallang/Whampoa, Pasir Ris, Queenstown, Serangoon, Tampines, Toa Payoh, Woodlands, Yishun; and 11 Other Estates: Central Area, Bukit Timah, Changi Village, Farrer Road, Jalan Kayu Rural Centre, Lim Chu Kang Rural Centre, Marine Parade, Pine Grove, Punggol Rural Centre, Sembawang, Tanjong Rhu / Mounthatten.
- AR 1994 reduced number of Other Estates to 6: Central Area, Bukit Timah, Sengkang, Lim Chu Kang, Marine Parade, Sembawang. New Towns became simply Towns.
- AR 1996 moved Sembawang and Sengkang from Other Estates to Towns”.
- AR 1999 added Punggol town.
- Lim Chu Kang was demolished, leaving 23 towns and 3 estates, figure unchanged for almost 20 years.
- Tengah was announced in 2016 as 24th HDB Town. There is no relation between Planning Areas / Towns and historical development HDB New Towns / Estates.
HDB’s current 24 Towns and 3 Estates match URA planning areas with 2 exceptions:
- Kallang-Whampoa town stretch on 3 planning areas (Kallang, Whampoa, Novena).
- Pasir Ris town also include Changi Village (from Changi planning area).
More notes:
- Geylang, Kallang-Whampoa and Bukit Merah towns contains several HDB estates built inside original Singapore city so they are not “new towns” but HDB classify them as “town” since Annual Report 1990.
- Queenstown was de facto first new town (built outside city), but Toa Payoh New Town started in 1965 was the first officially named “New Town”.
- Central Area, Bukit Timah and Marine Parade appear in Annual Report under “other estates” and in HDB Resale Flat Prices e-service as “town”.
- Lim Chu Kang estate got SERS and was no longer occupied since 2001, but it appeared in HDB Resale Flat Prices e-service until 2009.
- Tengah was added in HDB Resale Flat Prices e-service in 2016, despite that first BTO was launched in November 2018 and only around 2026 the flats are expected to reach resale market.
Housing density
Since 1960 to 1990s all HDB towns were planned using a standard density of 200 dwelling units per hectare. Flat sizes were growing over the years, leading to a stupid situation: the blocks with big flats and wealthy residents were denser and their occupants did not had enough space to park their cars, while the 1-room rental flats had largest open spaces and empty carparks.
Somewhere in 1990s a new urban planning control was introduced: plot ratios (gross floor area divided by land area). To create a vibrant city, low-, medium and high-density areas were created. The ratios were revised and raised in Master Plan 1998, today most public housing are in 2.8 – 4.2 range, low-density condos are low as 1.4 while office buildings in Central Business District reach a plot ratio of 12.
